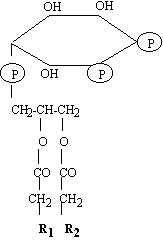
| In
1984, Lassing and Linberg, raised a few eyebrows by their discovery that
the well documented protein profilin, bound specifically to
phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate, (PIP2) a highly
charged phospholipid found at the cytoplasmic leaflet of the
plasma-membrane (Lassing &
Linberg, 1985) (Right).
This report was quickly followed by others who found that not
only did other ABPs bind these lipids, but that in doing so, their
actin-binding properties were modulated (e.g. Gelsolin see
below). The gelsolin cap at the end of the actin filament is very
tight but it was shown that PIP2
could dissociate the complex so that actin monomers can now leave
the barbed end of the filament (Janmey
et al, 1987a,
Janmey et al, 1987b).
|
 PIP2 PIP2 |
| References:-
Janmey, P. A., Chaponnier, C., Lind,
S. E., Zaner, K. S., Stossel, T. P. & Yin, H. L. (1985) Interactions
of gelsolin and gelsolin-actin complexes with actin. Effects of calcium
on actin nucleation, filament severing and end blocking., Biochemstry.
24, 3714-3723.
Janmey, P. A. & Stossel, T. P.
(1987a) Modulation of gelsolin function by phosphatidylinositol
4,5-bisphosphate, Nature. 325, 362-364.
Janmey, P. A., Iida, K., Yin, H. L.
& Stossel, T. P. (1987b) Polyphosphoinositide micelles and
polyphosphoinoositide-containing vesicles dissociate endogenous
gelsolin-actin complexes and promote actin assembly from the
fast-growing end of actin filaments blocked by gelsolin, J. Biol.
Chem. 262, 12228-12236.
Janmey, P. A., Lamb, J., Allen, P. G.
& Matsudaira, P. T. (1992) Phosphoinositide-binding peptides derived
from the sequences of gelsolin and villin, J. Biol. Chem. 267,
11818-11823.
Lassing, I. & Lindberg, U. (1985)
Specific interaction between phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and
profilactin, Nature. 314, 472-474. |
