|
Nebulin |
|
So
far the biggest actin binding protein not just in its size (600-900kDa) but in
that it binds a potential 200 actin monomers! Each monomer is bound by a 35
amino acid residue that may also bind calmodulin, tropomyosin and troponin (Wang
et al, 1996), and the N-terminal region
binds tropomodulin (McElhinny
et al, 2001).
The actin-binding core of the repeat is around a conserved motif SDxxYK (Pfuhl
et al, 1994), and this is proposed to bind
actin through a cleft formed "behind" sub-domains 3 and 4 of
actin in the standard view (Kabsch et al,
1990). Models have been proposed (Wang,
1999) in which it is suggested that nebulin co-aligns
with tropomyosin and troponn to form a multifilament that wraps around the thin
filament. However, the model suggested by (Pfuhl
et al, 1994) would seem to contradict this
view as the proposed nebulin site is distinct from tropomysoin.
|
|
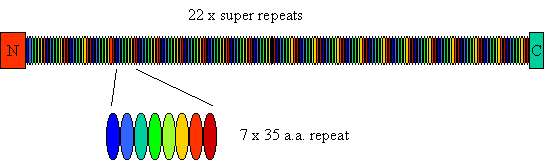
Figure 1. The Structure of Nebulin. 7x 35
amino-acid repeats form a unit that is itself repeated about 22 times. The
N-terminal associates with tropomodulin and so the pointed end of the thin
filament the C-terminus binds components of the Z-disc.
|
|
The
interaction of nebulin with actin is Ca2+-calmodulin sensitive (Root
& Wang, 1994).
Nebulin is proposed to form a "molecular ruler" controlling the length
of the thin filament (Chen et al, 1993b),
as differences in the length of expressed nebulin corresponds to the length of
the sarcomere (Kruger et al, 1991;
Labiet et al, 1991). Nebulin
is associated with an autosomal recessive nemaline myopathy in humans (Pelin
et al, 1999).
Douglas
Root Lab UCLA Annalisa
Pastore EMBL Mark
Pfuhl University of Leicester
References:-
Atsuta, F., Sato, K., Maruyama, K. & Shimada, Y.
(1993) Distribution of connectin (titin), nebulin and a-actinin
at myotendinous junctions of chicken pectoralis muscles: an immunofluorescence
and immunoelectron microscopic study., J.Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 14,
511-517.
Bang, M. L., Mudry, R. E., McElhinny, A. S., Trombitas,
K., Geach, A. J., Yamasaki, R., Sorimachi, H., Granzier, H., Gregorio, C. C.
& Labeit, S. (2001) Myopalladin, a novel 145-kilodalton sarcomeric protein
with mutliple roles in Z-disc and I-band assemblies., J.Cell Biol. 153,
413-427.
Chen, M.-J. G., Shih, C.-L. & Wang, K. (1993a)
Nebulin as an actin zipper. A two-module nebulin fragment promotes actin
nucleation and stabilizes actin filaments, J. Biol. Chem. 268,
20327-20334.
Chen, M.-J. G., Shih, C.-L. & Wang, K. (1993b)
Nebulin as an actin ruler, J.Biol.Chem. 268, 20327-20334.
Kabsch, W., Mannherz, H. G., Suck, D., Pai, E.
F. & Holmes, K. C. (1990) Atomic structure of the actin-DNase I complex, Nature.
347, 37-44.
Kruger, M., Wright, J. & Wang, K. (1991)
Nebulin as a length regulator of thin filament length, nebulin size, and epitope
profile., J.Cell Biol. 115, 97-107.
Labiet, S., Gibson, T., Lakey, A., Leonard,
K., Zeviani, M., Knight, P., Wardale, J. & Trinick, J. (1991) Evidence that
nebulin is a protein-ruler in muscle thin filaments., FEBS letters. 282,
313-316.
Luo, G., Zhang, J. Q., Nguyen, T. P., Herrera, A. H.,
Paterson, B. & Horowits, R. (1997) Complete cDNA sequence and tissue
localization of N-RAP, a novel nebulin-related protein of striated muscle., Cell
Mot.Cytoskel. 38, 75-90.
McElhinny, A. S., Kolmerer, B., Fowler, V. M., Labeit,
S. & Gregorio, C. C. (2001) The N-terminal end of nebulin interacts with
tropomodulin at the pointed ends of the thin filaments., J.Biol.Chem. 276,
583-592.
Meng, Y., Yasunaga, T. & Wakkabayashi, T. (1995)
Determination of the protein components of native thin filaments isolated from
natural actomyosin: Nebulin and
a-actinin are
associated with actin filaments., J.Biochem. 118, 422-427.
Moncman, C. L. & Wang, K. (1999) Functional
dissection of nebulette demonstrates actin binding of nebulin-like repeats and
Z-line targeting of SH3 and linker domains., Cell Motility Cytoskeleton. 44,
1-22.
Nwe, T. M., Maruyama, K. & Shimada, Y. (1999)
Relation of nebulin and connectin (titin) to dynamics of actin in nascent
myofibrils of cultured skeletal muscle cells., Exp.Cell Res. 252, 33-40.
Pelin, K., Hilpela, P., Donner, K., Sewry, C., Akkari,
P. A., Wilton, S. D., Wattanasirichaigoon, D., Bang, M.-L., Centner, T.,
Henefeld, F., Odent, S., Fardeau, M., Urtizberea, J. A., Muntoni, F., Dubowitz,
V., Beggs, A. H., Laing, N. G., Labeit, S., De La Chapelle, A. &
Wallgren-Pettersson, C. (1999) Mutations in the nebulin gene associated with
autosomal recessive nemaline myopathy., PNAS. 96, 2305-2310.
Pfuhl, M., Winder, S. J., Castiglione Morelli, M. A.,
Labeit, S. & Pastore, A. (1996) Correlation between conformational and
binding properties of nebulin repeats, J.Mol.Biol. 257, 367-384.
Pfuhl, M., Winder, S. J. & Pastore, A. (1994)
Nebulin, a helical actin binding protein, EMBO J. 13, 1782-1789.
Root, D. D. & Wang, K. (1994) Calmodulin-sensitive
interaction of human nebulin fragments with actin and myosin, Biochemistry.
33, 12581-12591.
Tatsumi, R., Hattori, A. & Takahashi, K. (1992)
Purification and characterization of nebulin subfragments produced by 0.1mM CaCl2.,
J.Biochem. 112, 780-785.
Tatsumi, R. & Takahashi, K. (1992) Calcium-induced
fragmentation of skeletal muscle nebulin filaments, J.Biochem. 112,
775-777.
Wang, K., Kniper, M., Huang, Q.Q., van Heerden, A.,
Hsu, L., Gutierrez, G. (1996) J.Biol.Chem. 271, 4304-4314.
Wang, K. (1999) Nebulin. Guidebook to the
Cytoskeleton Sambrook & Tooze, Oxford Uni.Press. p109-p111.
Wright, J., Huang, Q.-Q. & Wang, K. (1993) Nebulin
is a full-length template of actin filaments in the skeletal muscle sarcomere:
an immunoelectron microscope study of its orientation and span with
site-directed monoclonal antibodies., J.Muscle Res.Cell Motility. 14,
476-483.
Zhang, J. Q., Weisenberg, A. & Horowits, R. (1998)
Expression and purification of large nebulin fragments and their interaction
with actin, Biophys.J. 74, 349-359.
Zhukarev, V., Sanger, J. M., Sanger, J. W., Goldman, Y.
E. & Shuman, H. (1997) Distribution and orientation of rhodamine-phalloidin
bound to thin filaments in skeletal and cardiac myofibrils, Cell Mot.Cytoskel.
37, 363-377.
|
|
